The most common periodontal diseases?
The most common periodontal diseases are gingivitis and periodontitis.
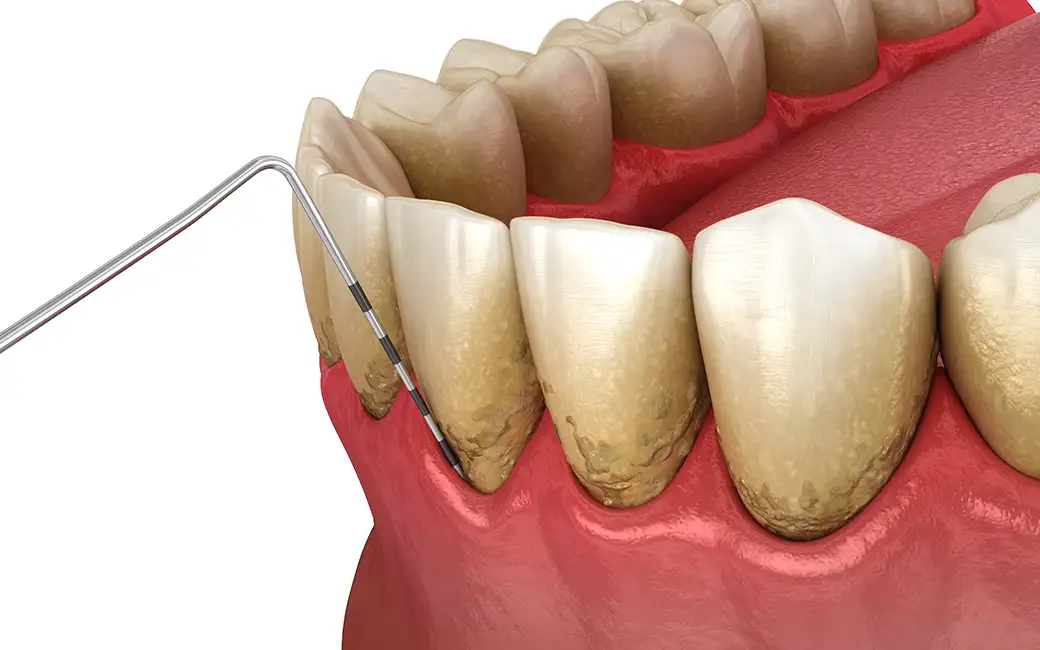
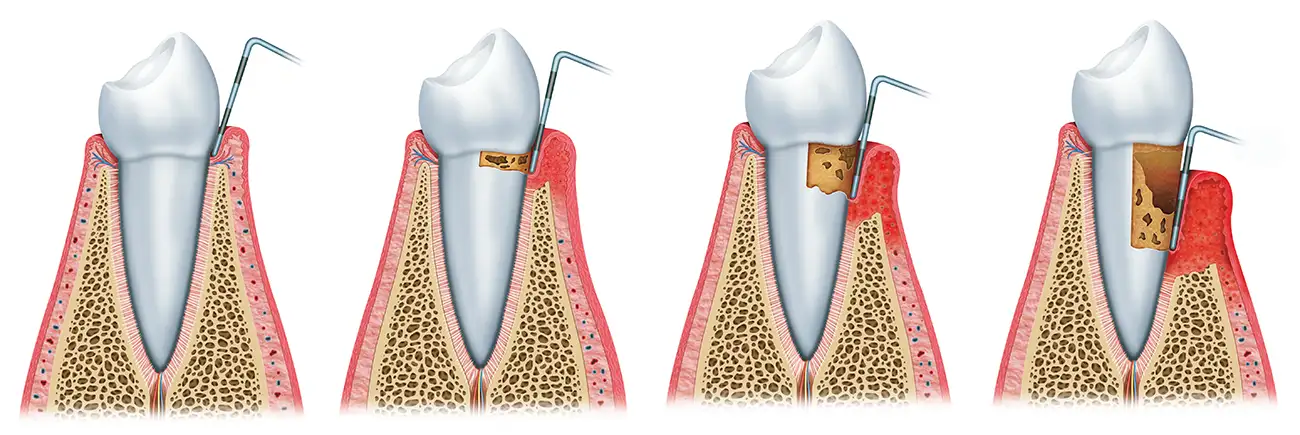
Gingiva is a tissue with a firm consistency of a light pink color that is located around the teeth. If there is a change in the color of the gingiva to a dark red or blue-purple color, it means that there has been inflammation of the gums or inflammation of the gingiva. Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease that causes inflammation and bleeding gums. Plaque build-up is usually the cause and can often be resolved with proper oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings.
Periodontitis is a progressive disease of the tissue that connects the root of the tooth to the bone and is located between the root of the tooth and the dental cup in which the tooth is located in the bone. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an infection of the tissues and bones that support the teeth. It is caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth and gums, which leads to inflammation, bleeding and eventually periodontitis.
Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gum disease that occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. This causes the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets that can become infected. The infection can damage the bones and supporting tissues of the tooth, leading to tooth loss if left untreated. It is often caused by a combination of plaque and tartar build-up, as well as other factors such as smoking, genetics and stress.
How to prevent periodontal diseases?
Periodontal diseases, or gum diseases, can be prevented by proper oral hygiene and regular teeth cleaning. Philia dental practice advises you:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles between teeth
- Use mouthwash because it provides protection by limiting dental plaque, strengthens teeth and tooth enamel, protects against caries, cleans interdental spaces and freshens breath.
- Regular visits to your dentist
- Quitting smoking and controlling alcohol consumption, as these habits can increase the risk of periodontal disease
- Eating healthy and avoiding sweets as this can lead to tooth decay
- Controlling any chronic health conditions, such as diabetes, that may affect your oral health
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise
- Control your stress levels
- Be aware of any warning signs of gum disease, such as red and swollen gums, receding gums, bad breath or loose teeth, bleeding gums, and seek treatment as soon as possible
How to treat periodontal diseases?
Periodontal diseases, also known as gum diseases, are caused by the accumulation of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums. Treatment options include:
- Professional cleaning – Deep cleaning of teeth and gums by a dentist
- Medicines – Antibiotics that can be prescribed to clear up the infection
- Surgery – In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue and restore gum health
- Lifestyle changes – Maintaining good oral hygiene, such as regular brushing and flossing
- Improve overall health – Risk factors for periodontal disease, such as smoking, diabetes and stress, should be managed to improve overall health and reduce the risk of recurrence
It is important to seek treatment from a dentist or periodontist if you suspect you have periodontal disease.
Don’t miss our promotions and advice..
Be the first to know.